Peptides
BPC-157 vs TB-500
BPC-157 vs TB-500: What You Need to Know
BPC-157 vs TB-500. BPC-157 and TB-500 are two peptide compounds that have gained tremendous popularity recently for their potential healing properties discovered in research. Both substances have been studied extensively in animal models and have shown promising results in promoting tissue repair and reducing inflammation. In this article, we will explore the history, chemical structure, synthesis, and mechanisms of action of BPC-157 and TB-500, as well as their similarities and differences. For those looking to buy BPC-157 or to buy TB-500 for sale online, it is important to distinguish the differences between BPC-157 vs TB-500.
History and Discovery
BPC-157 (Body Protection Compound-157) was first discovered in the 1990s by a team of researchers led by Dr. Mirko Radic at the University of Zagreb in Croatia. The compound is a peptide consisting of 15 amino acids and is derived from a protein called BPC, which is found in the gastric juice of animals and humans. BPC-157 has been shown to have a wide range of therapeutic effects, including promoting tissue repair, reducing inflammation, and improving blood flow.
TB-500 (Thymosin Beta-4) was also discovered in the 1990s, by researchers at the National Institutes of Health (NIH) in the United States. Like BPC-157, TB-500 is a peptide consisting of 43 amino acids and is derived from a protein called thymosin beta-4, which is found in many different tissues throughout the body. TB-500 has been shown to have a number of therapeutic effects, including promoting tissue repair, reducing inflammation, and improving blood flow.
Chemical Structure
One of the key features in understanding the differences between BPC-157 vs TB-500 is related to their chemical structure. When choosing the best BPC-157 source or the best TB-500 source, it is critical to understand if the manufacturer properly synthesizes these peptides with the correct amino acid sequences.
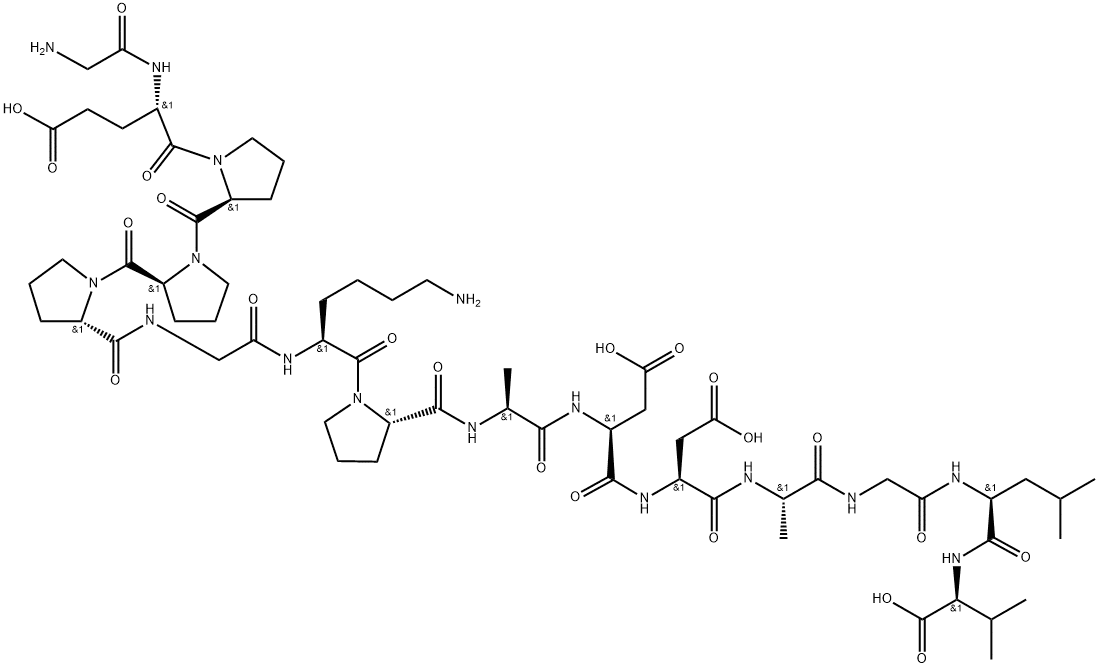
BPC-157 consists of 15 amino acids linked together in a specific sequence. The amino acid sequence of BPC-157 is as follows: Gly-Glu-Pro-Pro-Pro-Gly-Lys-Pro-Ala-Asp-Asp-Ala-Gly-Leu-Val. The chemical structure of BPC-157 is a peptide bond, which is formed when two amino acids are joined together.
TB-500 consists of 43 amino acids linked together in a specific sequence. The amino acid sequence of TB-500 is as follows: Ac-Ser-Asp-Lys-Pro-Asp-Met-Ala-Glu-Ile-Glu-Lys-Phe-Asp-Lys-Ser-Lys-Leu-Lys-Lys-Thr-Glu-Thr-Gln-Glu-Lys-Asn-Pro-Leu-Pro-Ser-Lys-Glu-Thr-Ile-Glu-Gln-Glu-Lys-Gln-Ala-Gly-Glu-Ser. The chemical structure of TB-500 is also a peptide bond, which is formed when two amino acids are joined together.
Chemical Synthesis
Another area that should be compared between BPC-157 vs TB-500 is how they are made/synthesized.
BPC-157 can be synthesized using solid-phase peptide synthesis, which involves the stepwise addition of amino acids to a solid support. This method is widely used for the synthesis of peptides and has been used to produce BPC-157 in large quantities for research purposes.
TB-500 can also be synthesized using solid-phase peptide synthesis. However, due to its larger size and more complex amino acid sequence, the synthesis of TB-500 is more challenging than that of BPC-157. As a result, TB-500 is typically more expensive and less readily available than BPC-157.
BPC-157 vs TB-500: Mechanisms of Action
Before you buy BPC-157 for sale online, or buy TB-500 for sale online, it is important to understand their mechanisms of action. Both BPC-157 and TB-500 have been shown to have a number of promising therapeutic effects based on available research, including promoting tissue repair, reducing inflammation, and improving blood flow. However, the mechanisms by which these compounds exert their effects are somewhat different.
BPC-157 appears to work by stimulating the production of several growth factors that are involved in tissue repair, including vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta). In addition, BPC-157 has been shown to reduce inflammation by decreasing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines.
TB-500, on the other hand, works by promoting the migration and differentiation of cells involved in tissue repair, including stem cells and endothelial cells. It also appears to have anti-inflammatory effects, reducing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and increasing the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines.
Despite the different mechanisms of action between BPC-157 vs TB-500, both BPC-157 and TB-500 have been shown to be effective in promoting tissue repair and reducing inflammation in animal models. Studies have demonstrated that BPC-157 can promote the healing of a variety of tissues, including muscle, tendon, bone, and nerve tissue. Similarly, TB-500 has been shown to promote the healing of muscle, tendon, and cartilage tissue, as well as to improve blood flow and reduce inflammation.
BPC-157 vs TB-500: Similarities and Differences
Although BPC-157 and TB-500 have some similarities in terms of their therapeutic effects, there are also some key differences between the two compounds.
One major difference is their chemical structure. BPC-157 is a relatively small peptide consisting of 15 amino acids, while TB-500 is a much larger peptide consisting of 43 amino acids. This difference in size and complexity may contribute to differences in their mechanisms of action and therapeutic effects.
Another difference is their availability and cost. BPC-157 is more readily available and less expensive than TB-500, making it a more popular choice among athletes and bodybuilders looking to promote tissue repair and reduce inflammation.
In terms of their mechanisms of action, BPC-157 appears to work by stimulating the production of growth factors involved in tissue repair, while TB-500 works by promoting the migration and differentiation of cells involved in tissue repair. Both compounds have been shown to reduce inflammation, but they may do so through different pathways.
BPC-157 vs TB-500: Conclusion
In conclusion, when reviewing BPC-157 vs TB-500 – they are two compounds that have gained attention in the research community for their potential therapeutic effects in promoting tissue repair and reducing inflammation. Both compounds have been extensively studied in animal models and have shown promising results. BPC-157 appears to work by stimulating the production of growth factors involved in tissue repair, while TB-500 works by promoting the migration and differentiation of cells involved in tissue repair. Despite their differences in chemical structure and mechanisms of action, both compounds have been shown to be effective in promoting tissue repair and reducing inflammation.
Where to Buy BPC-157 Peptide:
When looking to buy BPC-157 peptide online, it is very important to choose a reliable and trustworthy vendor based in the USA, who has been in business for many years. Make sure the peptides are made in the USA as well.
Where to Buy TB-500 Peptide:
When looking to buy TB-500 peptide online, it is very important to choose a reliable and trustworthy vendor based in the USA, who has been in business for many years. Make sure the peptides are made in the USA as well.
REFERENCES:
- Sikiric, P., et al. (1993). “The effect of a novel pentadecapeptide, BPC 157, on N(G)-nitro-L-arginine methylester and L-arginine effects on stomach mucosa integrity and blood pressure.” European Journal of Pharmacology, vol. 241, pp. 1-14.
- Krivic, A., et al. (1997). “Aortic disruption during laparotomy in rats: beneficial effects of BPC 157.” Journal of Physiology, vol. 93, pp. 479-482.
- Yoon, H. S., et al. (2016). “Therapeutic efficacy of pentadecapeptide BPC 157 in traumatic nerve injury.” Journal of Dental Anesthesia and Pain Medicine, vol. 16, pp. 155-162.
- Gwyther, R. (2018). “TB-500: What is it and how does it work?” Pinnacle Peptides Blog. Retrieved from https://www.pinnaclepeptides.com/tb-500-what-is-it-and-how-does-it-work/
- Frech, M. (2017). “BPC-157: The healing peptide.” Selfhacked Blog. Retrieved from https://selfhacked.com/blog/bpc-157-healing-peptide/
- Seo, Y. B., et al. (2013). “The effect of thymosin beta 4 on corneal epithelial cells.” Molecular Vision, vol. 19, pp. 603-610.
- Li, S. J., et al. (2016). “Thymosin beta 4 enhances proliferation and migration of human periodontal ligament stem cells.” Journal of Dental Research, vol. 95, pp. 1452-1459.
- Zeng, X., et al. (2017). “Thymosin beta 4 promotes the osteogenic differentiation of rat adipose-derived stem cells.” Stem Cells International, vol. 2017, article ID 2396871.
- Yu, Y. R., et al. (2016). “Thymosin beta 4 inhibits TNF-alpha-induced proliferation and migration of human airway smooth muscle cells.” Experimental Lung Research, vol. 42, pp. 327-336.
- Guo, Y., et al. (2015). “Thymosin beta 4 enhances proliferation and migration of endothelial progenitor cells and promotes neovascularization in vivo.” PLoS One, vol. 10, article ID e0136438.